A hallucination is a sensation or sensory perception that a person experiences in the absence of a relevant external stimulus. In simpler words, a person experiences something that doesn’t really exist (except in their mind). Hallucinations involve hearing, seeing, feeling, smelling, or even tasting things that are not real. Here are 10 different types of hallucinations that people can experience.
10. Excitation
Sometimes, something as simple as excitation can cause hallucinations. Feelings like anxiety can break the “normal” state of brain functioning and can trigger hallucinations. This kind of feeling do not happen in a calm state of mind, but by direct over-stimulation of the brain. Hallucinations through excitation or anxiety are a physiological response to the stress (or perceived stress) that the brain is experiencing and do not necessarily mean that there is an underlying mental illness. They can happen even to ordinary people under certain conditions.
9. Sleep Deprivation

People that have not slept for a long period of time may experience hallucinations. The reason is that the centers of the brain (and the neurons) that process their respective portions of our consciousness begin to degrade in these situations. Therefore, sleep deprivation causes an inability for the brain to create a unified experience of consciousness. In other words, you are not able to make reasonable sense of the stimuli from the outside world. In most cases, these hallucinations can be minor visual things that you see out of the corner of your eyes, but sometimes they become extreme and appear to be very real.
8. Hypnagogic Hallucinations
Hypnagogic hallucinations are imagined sensations that seem very real. The term hypnagogic defines the period when a person falls asleep and that’s why they are also referred to as sleep hallucinations. These hallucinations are relatively common in teenagers and young adults but this is something we grow out of with age for the most part. However, they can also be caused by narcolepsy, Parkinson’s disease or schizophrenia. The most common hypnagogic hallucinations are visual. They can include images of people, animals, or moving objects. In the more scary form, people can perceive bugs or insects crawling all over their bodies, which sometimes causes these individuals to itch, scratch, or make some other gestures to remove the hallucinatory objects from themselves.
7. Hypnopompic Hallucinations
The hypnopompic hallucinations occur in the state between waking up from sleep and being fully awake. One of the most common manifestations is the sleep paralysis. It is described as a terrifying experience often accompanied by sensing evil forces and fear. People often report that are being stepped on or attacked by some entity while they can’t move. The hallucinations also include ghosts, demons and other monstrous creatures. Scientists explain that the hypnopompic hallucinations are actually errors in the brain that happen when there is a problem with the REM (rapid eye movement) phase of sleeping.
6. Blindness (Charles Bonnet syndrome)
Visual hallucinations are often reported by the blind. They say that they are seeing things that are not there or that they are not capable of seeing. This form of hallucination is also known as the Charles Bonnet syndrome. It’s estimated that at around 20–30 percent of the visually impaired people have these hallucinations. Some individuals say that the experience is positive, even beautiful, while others find them terrifying. Scientists suggest that when you see real things around you, the information received from the eyes stops the brain from creating its own pictures. Losing the sight means that the brain will stop receiving so much information about the environment and it starts creating new fantasy images, patterns or old pictures that it has stored.
5. Sensory Deprivation
One of the most challenging, and unusual experiences is sensory deprivation. For example when the brain receives no sensory input for sound for a longer period of time, it will eventually begin to invent things that “should” be there. People who experienced this sensation have reported hearing voices inside their heads. This coincides with both the visual hallucinations of the blind and phantom limb syndrome, in which an amputee feels something in a part of the body which is gone. There are short-term sessions of sensory deprivation, which are described as relaxing and beneficial to meditation, however, extended or forced sensory deprivation can result in extreme anxiety, hallucinations, bizarre thoughts, temporary senselessness, and depression.
4. Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is a serious mental illness that interferes with a person’s ability to think clearly, manage emotions, make decisions and relate to others. One of the most common symptoms of schizophrenia is hallucinations. These include a person hearing voices, seeing things, or smelling things others can’t perceive. The hallucination is very real to the person experiencing it, and it may be very confusing for a loved one to witness. This illness often leads to delusional thinking and behaviors because the mind constantly misinterprets the inputs that the brain is receiving. It’s no wonder that the people who suffer from it lose sense of the reality.
3. Trance States (Autoscopy)
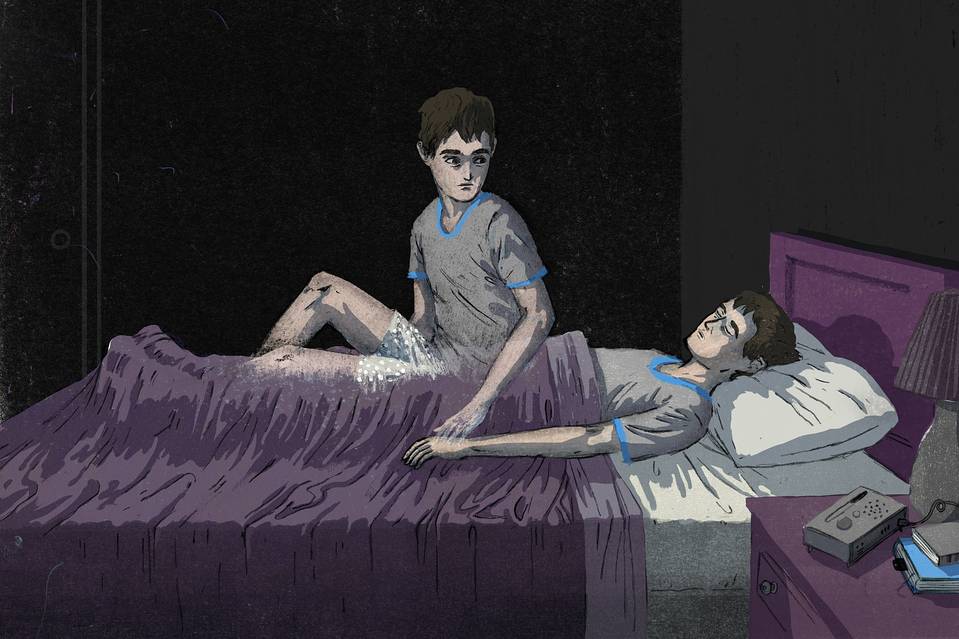

It’s said that people can achieve hallucinations simply by the power of their own minds. This can be accomplished in a deep state of trance and self-hypnosis. The process is called autoscopic hallucination. Autoscopy is the experience in which an individual perceives the surrounding environment from a different perspective, from a position outside of his or her own body. The term comes from the ancient Greek language and it literally means “self-watcher”. This type of experience is characterized by disembodiment – an apparent location of the self outside one’s body, impression of seeing the world from an elevated and distanced perspective and the impression of seeing your own body from this distanced perspective. According to some scientific researches, the autoscopic experiences are due to functional disintegration of lower-level multisensory processing and abnormal higher-level self-processing at the part of the brain known as the temporoparietal junction.
2. Epilepsy
According to a the latest scientific studies, epilepsy patients with damage to the left temporal cortex are at risk of experiencing complex, auditory verbal hallucinations. Epilepsy sufferers can have hallucinations accompanied by a fear of persecution or a feeling of being chased for some time before the onset of a seizure. Although the patient may not be conscious during the whole seizure, it is believed that he/she hallucinates the entire time. This type of seizure only affects one portion of the brain and can produce extremely complex and astonishing hallucinations.
- Drugs
Probably the most-known form of hallucinations is the use of drugs or similar substances that can have direct effect on the brain. The diverse group of drugs that can alter perception, thoughts, and feelings are called hallucinogens. They cause hallucinations, or sensations and images that seem real though they are not. Hallucinogens can be found in some plants and mushrooms or can be human-made. People have used them for centuries, mostly for religious rituals. The most popular drugs that cause hallucinations nowadays are LSD and psilocybin mushrooms. Research suggests that hallucinogens work by temporarily disrupting communication between brain chemical systems throughout the brain and spinal cord. Along with hallucinations, other short-term general effects include increased heart rate, nausea, intensified feelings and sensory experiences and changes in sense of time. Long-term consumption of hallucinogens can cause speech problems, memory loss, weight loss, anxiety, depression and paranoia.