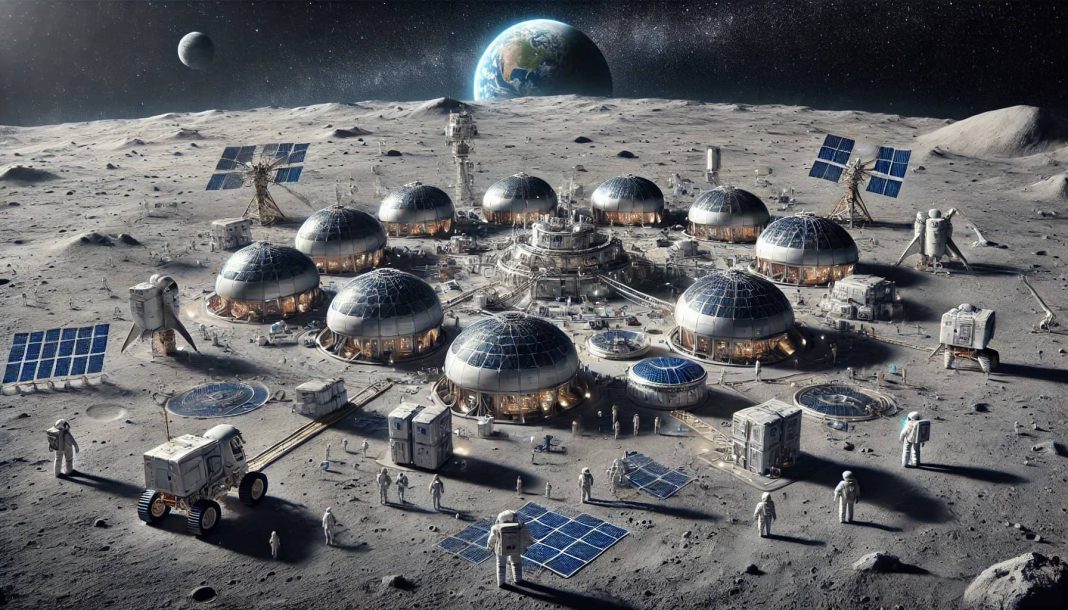
However, recent advancements in space technology and a growing interest in sustainable exploration have reignited enthusiasm for the Moon. NASA’s Artemis program, for example, aims not only to return humans to the lunar surface but also to establish a sustainable presence there. This shift from exploration to industrialization marks a significant turning point in humanity’s relationship with the Moon.
Why the Moon?
Strategic Location
The Moon’s proximity to Earth makes it an ideal candidate for a space hub. It’s close enough for relatively quick travel—taking just a few days—and communication delays are minimal. This makes it a perfect stepping stone for missions to more distant locations, such as Mars or asteroids.
Resource Potential
The Moon is rich in resources that could be vital for both space exploration and Earth-based industries. One of the most talked-about resources is helium-3, a potential fuel for nuclear fusion reactors. Additionally, the Moon’s regolith contains water ice, which can be converted into oxygen and hydrogen—essential for life support and rocket fuel. Mining these resources could drastically reduce the cost of space missions by enabling in-situ resource utilization.
Scientific Opportunities
The Moon also offers unique scientific opportunities. Its lack of atmosphere makes it an excellent location for astronomical observatories. Telescopes placed on the far side of the Moon could observe the universe without interference from Earth’s atmosphere or radio signals. Additionally, studying the Moon’s geology can provide insights into the history of our solar system.
Technological Developments Driving Lunar Industrialization
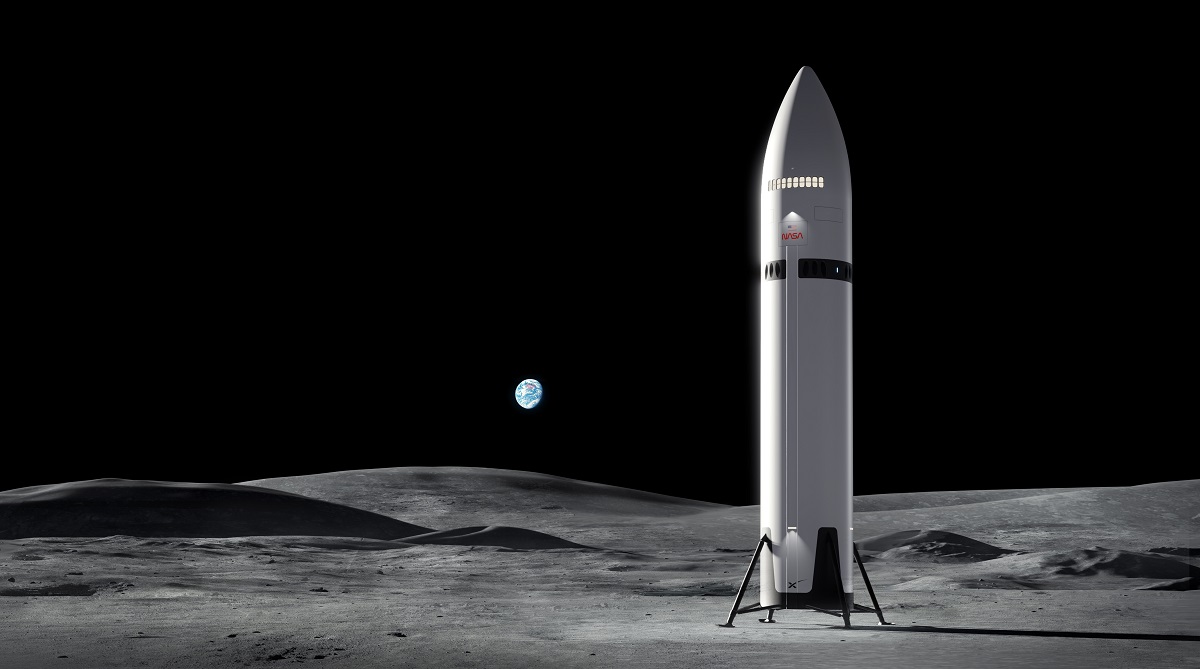
Reusable Rockets
Companies like SpaceX and Blue Origin have revolutionized space travel with reusable rocket technology. SpaceX’s Starship, for example, is designed to carry heavy payloads to the Moon and beyond, making lunar industrialization more economically viable.
Lunar Infrastructure
The development of infrastructure on the Moon is a critical step. NASA’s Lunar Gateway, a planned orbiting space station, will serve as a staging point for lunar operations. On the surface, habitats, power systems, and communication networks are being designed to support long-term human presence.
Resource Extraction Technologies
Advancements in robotics and autonomous systems are enabling the efficient extraction and processing of lunar resources. Robotic miners could harvest regolith to produce building materials, water, and fuel. These technologies are being tested in Earth-based simulations to prepare for deployment on the Moon.
International Collaboration
The effort to industrialize the Moon is a global one. NASA’s Artemis Accords aim to establish principles for international cooperation in lunar exploration. Countries like China, India, and Russia are also pursuing their own lunar programs. Private companies are playing a significant role as well, partnering with national space agencies to develop technologies and conduct missions.
While collaboration is key, the prospect of lunar resources also raises questions about governance and regulation. Who has the right to mine the Moon? How will conflicts be resolved? The answers to these questions will shape the future of lunar industrialization.
Ethical and Environmental Considerations
The industrialization of the Moon raises ethical and environmental concerns. The Moon’s pristine environment could be disrupted by mining and infrastructure development. Protecting its scientific and cultural value will require careful planning and regulation. Balancing exploration and preservation will be a major challenge as humanity expands its presence on the Moon.
The Economic Implications
The economic potential of the Moon is enormous. By enabling in-situ resource utilization, lunar industrialization could lower the cost of space exploration and open new markets. The development of lunar infrastructure could also spur innovation and create jobs on Earth. However, the high initial investment and technological challenges mean that significant risks remain.
The Path Forward
The industrialization of the Moon represents a critical step in humanity’s journey into the cosmos. By building a sustainable presence on the Moon, we can unlock new opportunities for exploration, science, and commerce. Through innovation, collaboration, and responsible stewardship, humanity can turn the Moon into a cornerstone of our extraterrestrial future.


















